Printing Related Settings
Printing via MyQ Roger is possible using these methods:
Printing from USB – The USB drive has to be connected to the device with the file for printing. It is only possible to print pdf and jpg files from USB.
Printing from Cloud – The Cloud storage has to be connected to the account. Currently it is not possible to browse Cloud storages from the device panel; printed files have to be uploaded via the mobile device. It is only possible to print pdf and jpg files from Cloud storage. The Size parameter can be used in the Mobile app only for pdf files.
Printing from the mobile application – For printing from the mobile application at least one Cloud storage has to be connected to the account for storing the jobs. The Size parameter can be used in the Mobile app only for pdf files.
Printing via MyQ Roger Client – No special settings needed on the terminal side. For the MyQ Roger Client configuration, check the MyQ Roger Client for Win manual.
Printing via Universal Print – No special settings needed on the terminal side. For the Universal Print configuration, check the MyQ Roger Server Administration manual, chapter 3.4 Universal Print. It is not possible to set paper size for Universal Print jobs. The Cassette 1 paper size is used for Universal Print jobs.
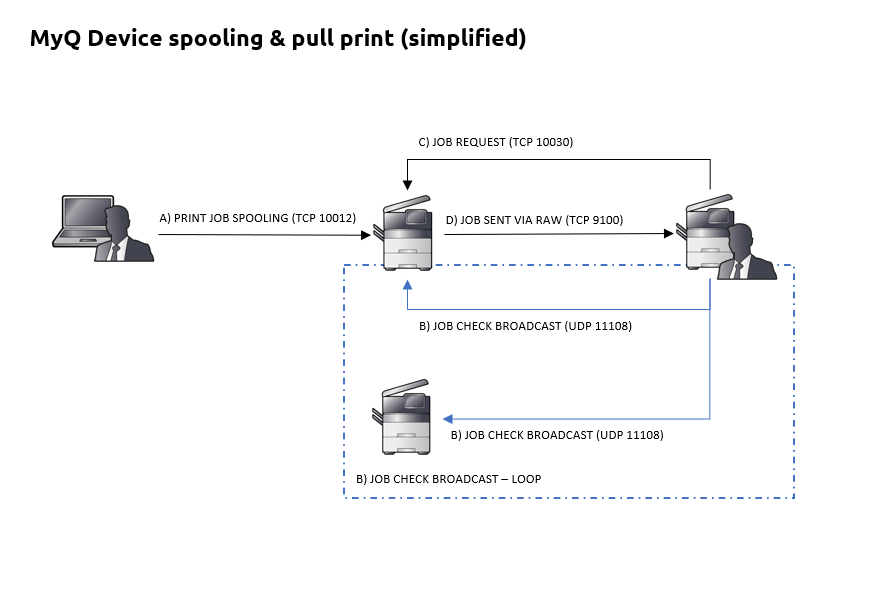
Printing via Device Spool – where all jobs are stored on the device’s HDD. Jobs sent to one printing device can be printed on any other printing device connected to the same local area network. If there are more mutually connected devices at the branch, the jobs spooled on the devices can be shared between them. In such cases, jobs sent to one device are displayed on the list of print jobs and can be printed on other devices.
Once the user logs on any of the devices connected to the same subnet, information about this job is provided and the job is displayed in the list of the available jobs and can be printed.
Windows Settings
You have to create a new print driver port and set the port protocol and port number.
Go to Windows Control Panel and open Devices and Printers. On the top ribbon, click Add a printer.
Windows automatically searches for devices.However, click The Printer that I want isn’t listed instead.
In the Add Printer window, select Add a local printer or network printer with manual settings, and click Next.
Under Choose a printer port, select Create a new port, and in the Type of port, select Standard TCP/IP Port, and click Next.
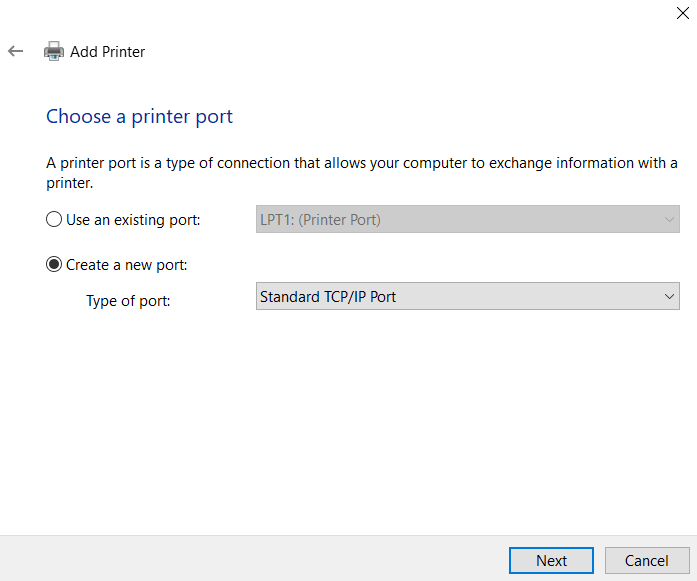
In the next window, type the
Hostname or IP addressof the printing device, and on the Port Name, add anamefor the port.Make sure that the Query the printer and automatically select the driver to use option is not checked and click Next.
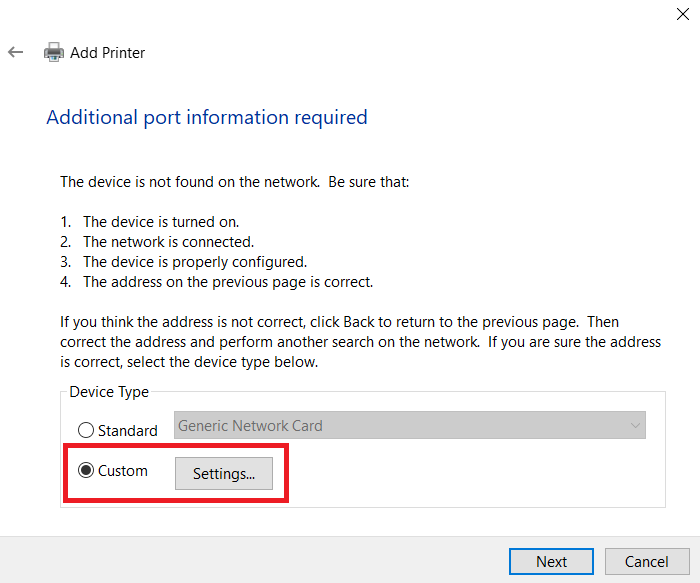
Wait for the detection to fail, and in the next window, select Custom and click Settings.
In the Printer Name or IP Address field, set the
hostname or IP addressof the printing device in your network.When configuring the port, use the Raw protocol and the 10012 port for pull printing (** check the full list of communication protocols and ports below).
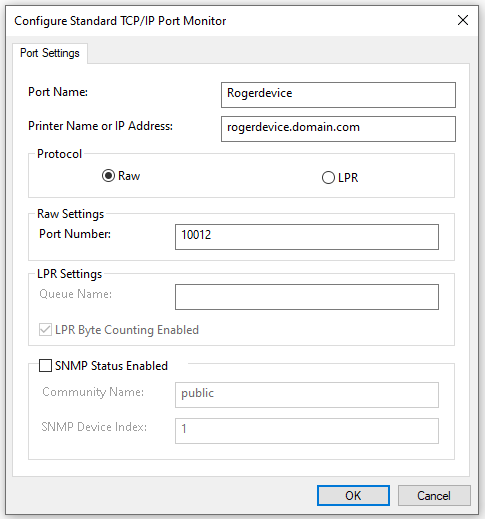
Once you configure the Port Settings, click OK, and then click Next.
Select your printer driver based on your printer model or use the printer’s CD/DVD setup kit. After that, click Next.
If you already have this printer driver, you are asked whether you want to replace it.Select Replace the current driver and click Next.
Add a
Printer nameand click Next.In the Printer Sharing window, choose whether you want to share this printer or not, and click Next.
Mark the Set as the default printer checkbox if you want to make this the default printer and click Finish.
MacOS Settings
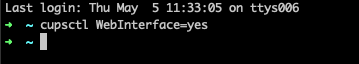
Navigate to the CUPS web UI: http://localhost:631
If disabled, you need to enable it by entering “cupsctl WebInterface=yes” to the terminal on your Mac.
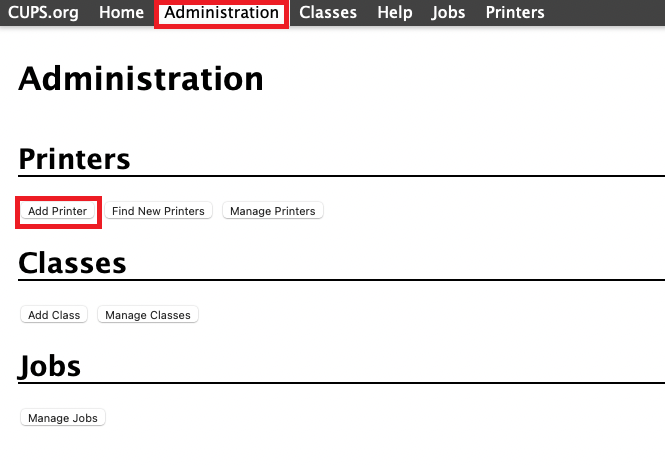
On the CUPS web UI, go to Administration in the top bar, and click Add Printer.
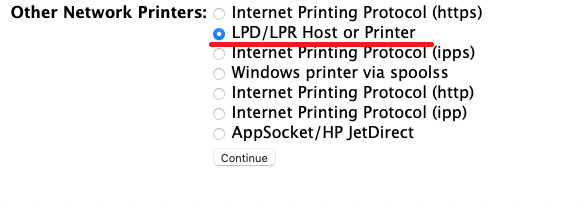
On this page, ignore any discovered printers, select the LPD/LPR Host or Printer option, and click Continue.
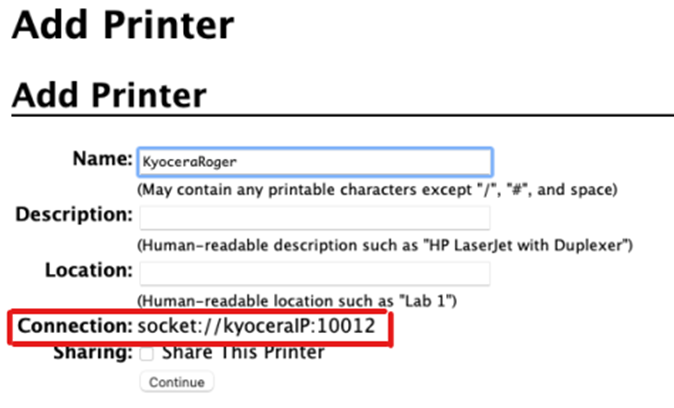
In Connection, type: socket://[hostnameOrIP]:10012
Where [hostnameOrIP]:port sets the hostname or IP address of the printing device in your network and the port you want to use, e.g.socket://10.14.4.25:10012.Click Continue (** Check the full list of communication protocols and ports below).
In the next page, fill in the Name and Location information, and click Continue.
Select the Kyocera Driver for the given model and click Continue.
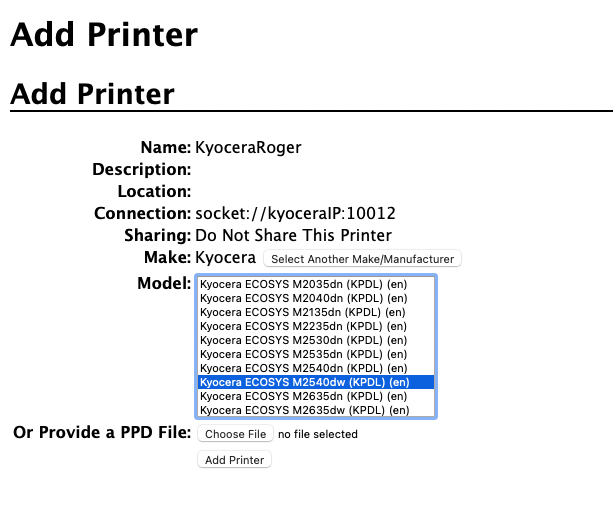
On the next page, fill in the default options for the given model, and click Set default options.
The printer is now available in your printers list as a standard printer.
** Full list of communication protocols and ports
Protocol | Port | Description |
|---|---|---|
TCP (IN/OUT) | 11108 | TCP link to device. Usage: Receive requests from Package. |
TCP (IN) | 10040 | Usage: Use printer as a proxy for TCP communication. |
UDP (IN) | 11108 | UDP Link to device. Multipurpose. It dispatches all the received UDP packages. Usage: Receive requests to get local jobs. |
UDP (OUT) | 11108 | Send broadcast to printers. GetJobs (Local Spooling) |
TCP (IN/OUT) | 10030 | TCP link to device. Usage: Receive requests or responses from other devices. |
TCP (IN) | 10011 | Usage: Receive raw data of print jobs for local hold job. The job is spooled by the printer and waits there until the user logs in and prints it. It is not possible to print this job on any other than this particular printing device. |
TCP (IN) | 10013 | Usage: Receive raw data of print jobs for local delegated job. |
TCP (IN) | 10020 | Usage: Receive raw data of print jobs for local LPR jobs. |
TCP (IN) | 10012 | Usage: Receive raw data of print jobs for local pull print jobs (Pull Print). |
Note: Other ports used by the printer (common for all printers. E.g. 9100 for raw printing, etc.). | ||
